FREE RADICAL REACTIONS
Refer to organic reaction mechanisms
COMMON RADICAL INIATORS:
UV light, Br2, Cl2, I2, SmI2, O2(triplet) , etc.
RADICAL INIATORS:
- UV light and a halogen molecule Br2, Cl2, or I2,
e.g. Br2 + UV light ____> Br* + Br *
can be written as,
Br-Br + UV light _____> Br* + Br *
- Single electron donors such Samarium iodide [ SmI2 ]
It is an ionic compound that has samarium with 4 unpaired valence electrons available for donation.
CH3Cl + SmI2 _____> *CH3 + SmI2Cl
CH3HC=O + SmI2 _______> CH3HC*-O:SmI2
Can be written as
CH3HC=O + SmI2 _______> CH3HC*-O-SmI2
Two equivalents of single electron donors will give two electrons to any species to form nucleophilic.
e.g CH3Cl + 2SmI2 _____> + SmI2Cl + I2Sm:CH3
can be written as
CH3Cl + 2SmI2 _____> + SmI2Cl + I2Sm-CH3 [methyl nucleophilic agent]
- Reactions of Sodium or lithium in liquid ammonia involves initial donation of an electron to another specie to form a radical but the specie receives another electron to form an anion.
- Na + A ______> Na + + A* [radical]
- Na + A* ______> Na + + A** can be written as {anion A–}
- Triplet oxygen [ O2(triplet) *O-O* etc.
It does not readily function as common radical initiator but very reactive with other free radicals.
Common radical reactions
Free radical mechanism usually involves 3 steps: initiation, propagation and termination(combination).
Examples
Long term degradation of methylene chloride to HCl and other gases when exposed to sunlight.
2CH3Cl + UV light + 4Cl2 ________> 2CHCl3 + 4HCl
2CH3Cl + UV light + Cl2 ________> 2HCl + 2CH2Cl2
Mechanism
Initiation
Cl2 + UV Light _____> Cl * + Cl *
illustration by half arrow mechanism
Propagation reactions [illustration only ]
CH3Cl + Cl * ________> *CH3 + Cl2

CH3Cl + Cl *________> HCl + *CH2Cl
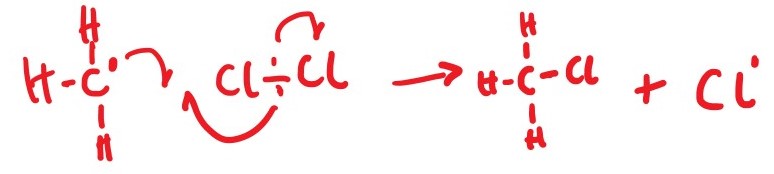
*CH2Cl + HCl ________> CH3Cl + Cl
*CH3 + Cl2 ________> CH3Cl + Cl
*CH3 + HCl ________> CH4 + Cl
CH4 + *CH2Cl________> *CH3 + CH3Cl
CH3Cl + *CH2Cl________> CH2Cl2 + *CH3
*CH2Cl + Cl2 ________> CH2Cl2 + Cl*
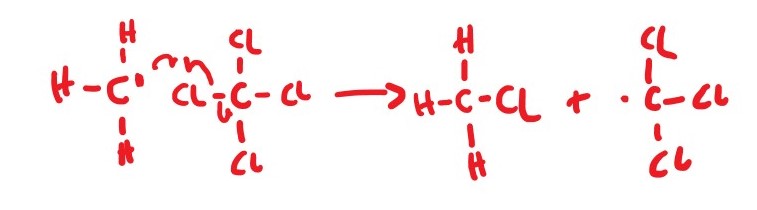
CH2Cl2 + Cl *________> *CHCl2 +HCl
Cl2 + *CHCl2 ________> CHCl3 + Cl *
CHCl3 + Cl * ________> *CCl3 + HCl
Cl2+ * CCl3 ________> CCl4 + Cl*
*CH3 + CCl4 ________> *CCl3 + CH3Cl
TERMINATION / COMBINATION
Cl* + * CCl3 ________> CCl4
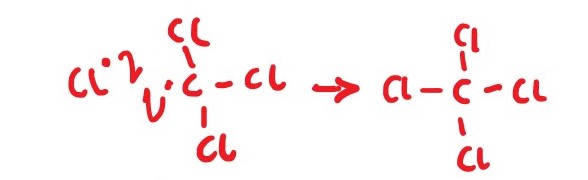
Cl * + *CHCl2 ________> CHCl3
Cl * + *CH2Cl ________> CH2Cl2
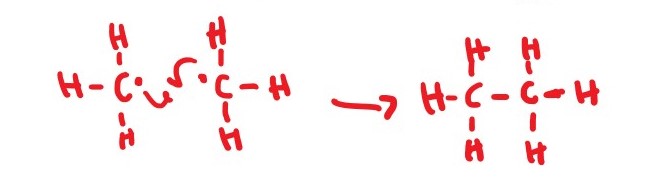
*CH3 + Cl * ________> CH3Cl
*CH3 + *CH3 ________> CH3CH3